Simple Discrete Systems
– Microstates and macrostates.
– The N-coin model, probabilities of microstates and
macrostates with fair coins,
prob(n) = Ω(N)
/ Ω(all), with Ω(n)
= (N choose n).
– The N-spin paramagnet, counting microstates corresponding to
a macrostate.
– The Einstein model of a solid, N oscillators, each with energy
equal
to a multiple of hf,
Ω(N, q)
= (q+N–1 choose q).
The Ideal Gas
– Setting up the calculation of the multiplicity of microstates
for given N and U, Ω(N,U)
= f(N) V N U 3N/2.
– Gaussian form of the multiplicity Ω(NA,UA; NB,UB)
for fixed U = UA + UB.
Statistical Mechanics, Heat Flow and the Second Law
– The fundamental assumption of statistical mechanics.
– Behavior of Ωtotal = ΩAΩB for
a system consisting of subsystems A and B.
– The second law of thermodynamics in terms of multiplicities, statistical
origin.
Entropy
– Small, large, and very large numbers; Stirling's approximation,
N! = N N e–N (2πN)1/2 and ln N!
= N ln N – N.
– Concept and definition of entropy,
S = k ln Ω.
– The second law of thermodynamics in terms of entropy.
– Entropy growth, reversible and irreversible processes.
– Calculating S starting from 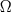 in
examples, including entropy of mixing. in
examples, including entropy of mixing. |