Chapter 29: Magnetic Fields
- Magnetic force: On a moving charge F = q v × B, on a current F = I L × B, or F = ILB sinθ.
- Path of a particle: In a constant magnetic field, a particle moves on a circle with r = mv/|q|B.
- Torque on a current loop: The magnetic dipole moment and torque on the loop are τ = μ × B, μ = NIA .
Chapter 30: Sources of the Magnetic Field
- Biot-Savart law: For a wire element ds, dB = (μ0/4π) (I ds × r)/r2 , where μ0 = 4π × 10–7 T·m/A.
- Examples: For a long straight wire, B = (μ0/2π) I/r ; For a circular wire B = (μ0/4π) I φ/r .
- Magnetic force between wires carrying currents: For two long straight wires F = (μ0/2π) (I1I2/a) L .
- Ampère's law: For any closed loop C in space enclosing a current Ienc, ∫C B · ds = μ0 Ienc .
- Magnetic field of a long solenoid: The magnitude of the field is B = μ0nI (n = N/L) .
Chapter 31: Faraday's Law
- Magnetic flux: The flux of B through a surface S is ΦB = ∫S B · dA .
- Faraday's law: When ΦB changes in time,
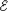 =
–N dΦB/dt
, or ∫C E · ds =
– dΦB/dt
.
=
–N dΦB/dt
, or ∫C E · ds =
– dΦB/dt
. - Motional emf: The potential difference induced across a moving conductor,
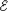 = –Blv .
= –Blv .
Chapter 34: Electromagnetic Waves
- Maxwell's equations: They contain all information on how electric and magnetic fields are produced,
- Electromagnetic waves: Plane harmonic waves E = Emax cos(kx – ωt) and B = Bmax cos(kx – ωt),
with k = 2π/λ, ω = 2πf and, as for all waves, λf = v, the speed; E/B = c, c = (μ0ε0)–1/2 = 3.00 × 108 m/s . - Energy, momentum: Poynting vector S = (1/μ0) E × B, P = S/c or 2S/c (absorbing or reflecting surface).
∫S E · dA = qenc/ε0 , ∫C E · ds = – dΦB/dt , ∫S B · dA = 0 , ∫C B · ds = μ0Ienc + μ0ε0 dΦE/dt .
Chapter 35, 36: The Nature of Light and Ray Optics, and Image Formation
- Reflection: The law of reflection, θ1' = θ1 .
- Refraction: Index of refraction n = c/v; The law of refraction, n1 sin θ1 = n2 sin θ2 .
- Curved mirrors: Focal length f = R/2; Mirror equation 1/p + 1/q = 1/f ; and M = h'/h = –q/p.
Chapters 37, 38: Wave Optics and Diffraction Patterns and Polarization
- Interference pattern: For two thin slits, bright fringes are located at d sin θ = mλ, with m = 0, ±1, ±2, ...
- Diffraction pattern: For a narrow slit, dark fringes are located at a sin θ = mλ, with m = ±1, ±2, ...
Chapters 39, 40: Relativity and Introduction to Quantum Physics
- Length contraction, time dilation: L = Lp/ γ, and Δt = γ Δtp, γ = 1/(1–v2/c2)1/2.
- Light as particles: E = hf , where h = 6.63 × 10–34 J·s is Planck's constant; Wavelength λ = h/p.
- Uncertainty principle: Δx Δp ≥ (1/2) h/2π.