Chapter 23: Electric Fields
- Coulomb's law: F = k q1q2/r 2 = 1/(4πε0) q/r 2, k = 8.99 · 109 N·m2/C2, ε0 = 8.85 × 10–12 C2/N·m2.
- Fundamental charge: Value of the charge of an electron or proton, e = 1.60 × 10–19 C .
- Electric field: E = F/q ; For a point charge, E = k q/r 2 = 1/(4πε0) q/r 2.
- Electric field due to a charge distribution: Sum individual contributions or integrate, E = k ∫ (dq/r3) r .
Chapter 24: Gauss' Law
- Electric flux: For constant E, flat surface, ΦE = (E cosθ) A = E · A. In general, ΦE = ∫ E · dA .
- Gauss' law: The electric flux through a closed Gaussian surface is ΦE = qin/ε0.
- At the surface of a conductor: It has to be perpendicular to the surface, and its magnitude is E = σ/ε0.
- Large plate: Non-conducting E = σ/2ε0 on both sides; Between plates with opposite charges, E = σ/ε0.
Chapter 25: Electric Potential
- Electric potential energy: As for any conservative force, U = –WPO.
- Electric potential: Defined as V = U/q = –WPO/q ; In terms of E, V(P) = –∫ E · ds and Es = –∂V/∂s .
- Examples: For a point charge V = k q/r ; Potential energy of a 2-point-charge system U = k q1q2/r ; For a charge distribution add the single-charge contributions, or set up an integral, V = k ∫ dq/r .
Chapter 26: Capacitance and Dielectrics
- Capacitance: Defined by C = Q/V ; For a parallel-plate capacitor, C = ε0A/d.
- Capacitor combinations: In series, Ceq–1 = C1–1 + C2–1 + ...; In parallel, Ceq = C1 + C2 + ...
- Electric energy: In a capacitor, U =
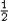 QV ;
Energy density in an electric field u = U/volume
=
QV ;
Energy density in an electric field u = U/volume
= 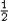 ε0E2.
ε0E2. - Dielectrics: The permittivity of the vacuum gets replaced by ε = ε0κ; For example, C = ε A/d = κε0 A/d.
Chapter 27: Current and Resistance
- Electric current: I = dQ/dt , or Q = ∫ I(t) dt ; Current density defined by I = ∫ J · dA; Also, J = nevd.
- Ohm's law: Relationship between potential difference and current, I = V/R ; also E = ρJ, or J = σE.
- Resistance: For a uniform block of length L and cross-sectional area A, R = ρL/A .
- Power: In general, P = IV. For current through a resistor, P = I2R = V2/R.
Chapter 28: Direct-Current Circuits
- Emf: The amount of amount
of work done per unit charge
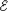 =
dW/dq; With internal resistance V =
=
dW/dq; With internal resistance V = 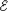 – Ir.
– Ir. - Resistor combinations: In series Req = R1 + R2 + ...; In parallel Req–1 = R1–1 + R2–1 + ...
- RC circuits: τ = RC; Charge V(t) = V0 (1 – e–t/RC) and q(t) = Q (1 – e–t/RC); DischargeV(t) = V0 e–t/RC .