Chapter 28: Direct-Current Circuits
- Emf: For a battery or other power source, the amount of amount
of work done per unit charge to force a current through the circuit,
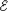 =
dW/dq . =
dW/dq .
- Internal resistance: All batteries have a small
internal resistance r,
which can be treated as in series with the battery itself; This implies
that the actual terminal voltage V is related to the battery
emf
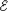 by by
V = 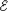 – Ir . – Ir .
- Potential differences: Finding the potential difference V across
an emf device or a resistor with a current I flowing through
it, and across a capacitor with a charge Q on it, including
the sign of V.
- Resistors in series: The resistance equivalent to R1, R2,
... in series is
Req = R1 + R2 +
...
- Resistors in parallel: The resistance equivalent to R1, R2,
... in parallel is obtained from
Req–1 = R1–1 + R2–1 +
...
- Kirchhoff's laws: Statement and use of the loop rule and the
junction rule.
- RC circuits: The time constant is τ =
RC; What happens to the charge across a capacitor and the
current through a resistor when the capacitor is being charged or discharged.
Charging the capacitor: The voltage varies in time according to
V(t) = V0 (1 – e–t/RC)
; similarly, for the charge, q(t) = Q (1 – e–t/RC)
.
Discharging the capacitor: The voltage varies
in time according to
V(t) = V0 e–t/RC .
|