Chapter 26: Capacitance and Dielectrics
- Capacitors: General concept and use; The capacitance is defined by
C = q/V .
The unit is the farad, 1 F = 1 C/V.
- Parallel plate capacitors: C = ε0A/d,
where ε0 =
8.85 × 10–12 C2/N·m2 as
usual is the permittivity constant, related to the coefficient
in Coulomb's law by k = 1/(4πε0).
- Capacitors in series: The capacitance equivalent to C1, C2,
... in series is obtained from
Ceq–1 = C1–1 + C2–1 +
...
- Capacitors in parallel: The capacitance equivalent to C1, C2,
... in parallel is
Ceq = C1 + C2 +
...
- Electric energy: In a charged capacitor, U =
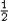 qV [same
as q2/2C and CV2/2].
This implies that in an electric field E in general, there
is an energy density u = U/volume
= qV [same
as q2/2C and CV2/2].
This implies that in an electric field E in general, there
is an energy density u = U/volume
= 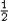 ε0E2. ε0E2.
- Dielectrics: Materials that become polarized in the presence
of electric fields; They modify the values of the E fields
and potentials produced by charges. As a result, effectively the
permittivity of the vacuum gets replaced everywhere by ε = ε0κ,
where κ is the dielectric constant. For example, the
capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor becomes
C = ε A/d
= κε0 A/d. |