Circular Motion
- Tangential acceleration: Meaning, and uniform vs non-uniform
circular motion.
- Centripetal acceleration: Concept, and relationship with speed,
aR = v2/r.
- Frequency and period: Concepts, and relationships between
them and with speed,
f = 1/T , v = 2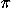 r/T . r/T . Gravitation
- Newton's law of gravitation: General form of the force of
gravity,
FG = G
m1m2/r2 .
- Near Earth's surface: Relating Newton's law of gravitation
with FG =
mg.
- Gravity in space: Is it zero in an orbiting spacecraft? Why
are astronauts "weightless"?
- Gravitational potential energy: In general, not necessarily
close to the Earth's surface,
PEG = –G
m1m2/r .
Solving Problems
- String tensions and normal forces: Finding how they vary in
vertical circular motion.
- Highway curves: Using friction in connection with radial acceleration.
- Gravity: Using vectors to calculate the force of gravity due
to various objects.
- Satellite motion: Relating the period of its orbit to the
orbit radius and the Earth's mass.
|