Linear Momentum
and Its Conservation
- Momentum: For a particle of mass m moving with velocity v, p = mv.
- Impulse: If a force F acts during a time
 t,
it imparts an impulse F t,
it imparts an impulse F  t. t.
- Relationships: The change in momentum of a particle is related
to the force or impulse on it,
F =  p/ p/ t , or t , or  p = F p = F  t . t .
- Conservation: The total momentum of a system of particles
is conserved if the system is isolated, no external forces
act on it.
Collisions (In 1 Dimension)
- Momentum: The total momentum of two particles is considered
to be conserved during a collision.
- Kinetic energy: The total kinetic energy of two particles
is conserved in an elastic collision, not in an inelastic collision;
Concept of totally inelastic collision.
- Problem solving: Be able to use conservation of linear momentum
and (whenever appropriate) conservation of kinetic energy in 1-dimensional
collision problems,
mAvA +
mBvB =
mAv'A + mBv'B ,
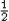 mAvA2
+ mAvA2
+ 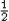 mBvB2 = mBvB2 =
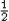 mAv'A2 + mAv'A2 + 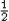 mBv'B2 . mBv'B2 .
Center of Mass
- Concepts: What are the center of mass and the center of gravity
of an object, or a set of objects? If the momentum of a system is
conserved, its CM moves with constant velocity
|