Newton's Laws of Motion
- First law: If the net force on a body is zero, it does not
accelerate (is its velocity zero?).
- Second law: The acceleration of an object is
related to the total force on it by Fnet = ma.
- Third law: If an object A exerts a force F on
an object B, then B exerts a force –F on
A.
Types of Forces
- Weight: Near the Earth's surface the gravitational force is
always FG = mg,
downwards.
- Normal force: A force that acts on an object in contact with
a solid surface. Perpendicular to the surface; its magnitude FN depends
on the situation, and can be found using the fact that the surface
prevents the body
from
sinking
into
it (up to the surface's breaking point).
- String tension: A force that acts on an object attached to
a string (cable, rope). It is directed along the string away from the
body, and its magnitude FT depends
on the situation
– up to the string's breaking point. The tension is the same
at all points
along a string, provided that no tangential forces (including the string's
own weight) are applied to the string.
- Friction: A force that acts on an object in contact with
a solid surface (we do not treat friction with air and other fluids).
It is along to the surface, and there are two types. Static friction:
Its value depends on the situation, but cannot exceed a maximum value, Fs
 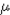 s FN. Sliding
friction:
(a.k.a. kinetic friction) Fk = s FN. Sliding
friction:
(a.k.a. kinetic friction) Fk = 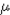 k FN. k FN.
- Elastic force: Exerted by a spring in the direction opposite
to the displacement, F = –kx.
Solving Problems
- Setup: Sketch of situation, choice of axes (may depend on
forces present), drawing of free-body diagram, resolving all forces
present along the two axes if relevant.
- Using Newton's laws: Writing down the equations, using the
information available (from the free-body diagram and the statement
of the problem).
- Kinematical aspects: Some problems require the use of equations
that relate the acceleration to other information on the motion.
Static Equilibrium Situations
- Concepts: What is equilibrium? Torque,
 =
rperp F. =
rperp F.
- Conditions for equilibrium: No net force and no net torque
on the object,
1st: Fnet =
0 ; 2nd:  net =
0 . net =
0 .
- Skills: Be able to solve static equilibrium problems in two
dimensions, using both conditions for equilibrium and (if necessary)
resolving forces into components.
|