Basic Concepts
and Effects
- Basic concepts: Periodic vibrations/oscillations (when do
they happen?); Displacement, amplitude A, period, frequency
(f =
1/T) and phase frequency
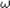 ; Simple harmonic oscillator. ; Simple harmonic oscillator.
- Damped oscillations: Concept; Underdamped and
overdamped oscillations.
- Forced oscillations: Concept; Natural frequency and resonance.
Object Attached to a Spring
- Force: Hooke's law, F = –kx.
- Mechanical energy: At an arbitrary point, E = KE + PE =
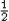 mv2 + mv2 +
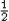 kx2 ;
Be able to relate E to the amplitude A and to the
vmax using the fact that E is
conserved. kx2 ;
Be able to relate E to the amplitude A and to the
vmax using the fact that E is
conserved.
- Period: T = 2
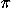 (m/k)1/2. (m/k)1/2.
- Position as a function of time: A sinusoidal function; The
most common forms are
x(t) = A cos(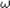 t) and A sin( t) and A sin(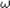 t)
. t)
.
Simple Pendulum
- Restoring force: Related to the angle by F = –mg sin
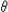 ; When can the motion of a simple pendulum be considered simple
harmonic motion? ; When can the motion of a simple pendulum be considered simple
harmonic motion?
- Period: T = 2
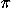 (L/g)1/2. (L/g)1/2.
|