|
Result
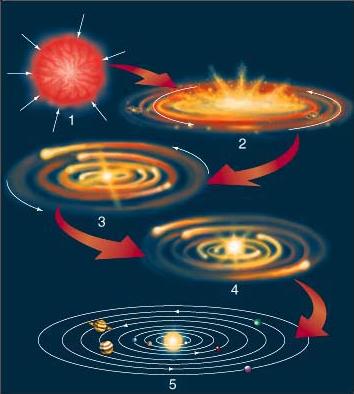
- Overview: After a billion years
of clean-up and meteoritic bombardment, you end up with ten or
so planets, in stable orbits; The protostar turned into a star
when the core became hot enough.
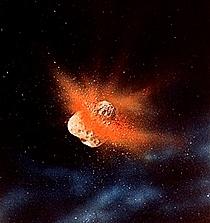
- Catastrophes: Needed to explain
specific isolated features and exceptions. The planets, their
surfaces and atmospheres may be heavily modified by the last,
big collision they experience.
- Examples: For Earth, our Moon
and the presence of water, brought by comets (the original Earth
could not have retained it); Also, composition of
Mercury, Venus' rotation, Uranus' tilt.
- Debris: Some planetesimals remain
in the asteroid belt (a would-be planet, if not for Jupiter)
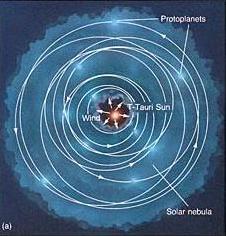
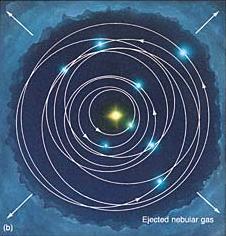
and the Kuiper belt; others are thrown outwards by "gravity
assist" during close encounters (Oort cloud); Some dust
remains in a dust disk in the plane of the solar system; we see
it from the zodiacal light it scatters..
- How big is it? Pluto's orbit
at 40 AU, Kuiper Belt between 30 and 100 AU or so, the Oort Cloud
extends out to 50,000-100,000; The nearest star is at about 300,000.
What Evidence Do We Have?
- Earth and Moon rocks: They can
be dated using their radioactive elements; The oldest ones are
about 4.5 billion years old.
- Meteorites: The oldest objects
in our solar system are 4.57-Gyr old, mm-sized grains
found in some meteorites; Some even give us evidence that a star
exploded in our neighborhood around the time the solar system
formed, and the Sun may have been part of a cluster.
- Exploration and experiments: Spacecraft
have been sent to observe asteroids made of "primitive rock" (like
NEAR, with asteroid Eros, and Hayabusa, to asteroid Itokawa) and
comets (Rosetta), and collect samples of solar wind (Genesis); Conditions
have been
recreated
in
a Space Shuttle flight.
- Solar neighborhood: Its configuration
also shows evidence for some kind of past explosion; For example,
we seem to be inside a bubble with walls about 70 light years
away; Further away, we can see
other (proto)planetary systems where the process is happening right now.
|
|



![]()