|
What Do We Easily See about Light?
|
|
External Links page. |
|
What Do We Easily See about Light?
|
|
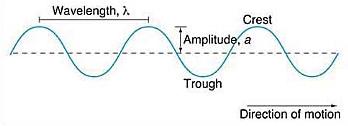
A Few Notions about Waves
|
 |
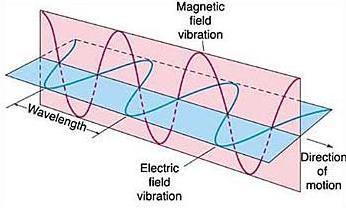 |
What Are Light and Radiation?
|
|
|
|
|
| Radio * (l from mm's to 1000's of m) | Radio, TV; Antennas | Radar studies of planets; Interstellar gas clouds; Active galaxies and galactic structure |
| Microwaves (l from mm's to cm's) | Cell phones; Ovens | Cosmic background radiation |
| Infrared * (l from microns to mm) | Communications, remote controls; Warm objects | Interstellar dust and star forming regions; Cool stars |
| Visible * (l from 400 to 700 nm) | Ordinary light; Hot objects | Solar system planets; Stars; Galaxies |
| Ultraviolet (l from 10–9 to 10–7 m) | Solar radiation; Atoms | Hot stars; Interstellar medium |
| X-rays (l from 10–11 to 10–8 m) | Medical applications; Atoms | Stellar atmospheres; Neutron stars and Black holes; Galaxy clusters; Active galactic nuclei |
| Gamma rays (l less than 10–11 m) |
Medical applications; Nuclear reactions | Neutron stars, cosmic ray collisions; Active galactic nuclei; Gamma Ray Bursts. |
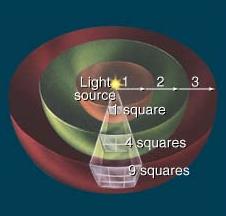 |
What Can We Learn from Analyzing Light?
|
|
Examples of Uses of Different Types of Radiation
|
![]()
page by luca bombelli <bombelli at olemiss.edu>, modified 10 sep 2012